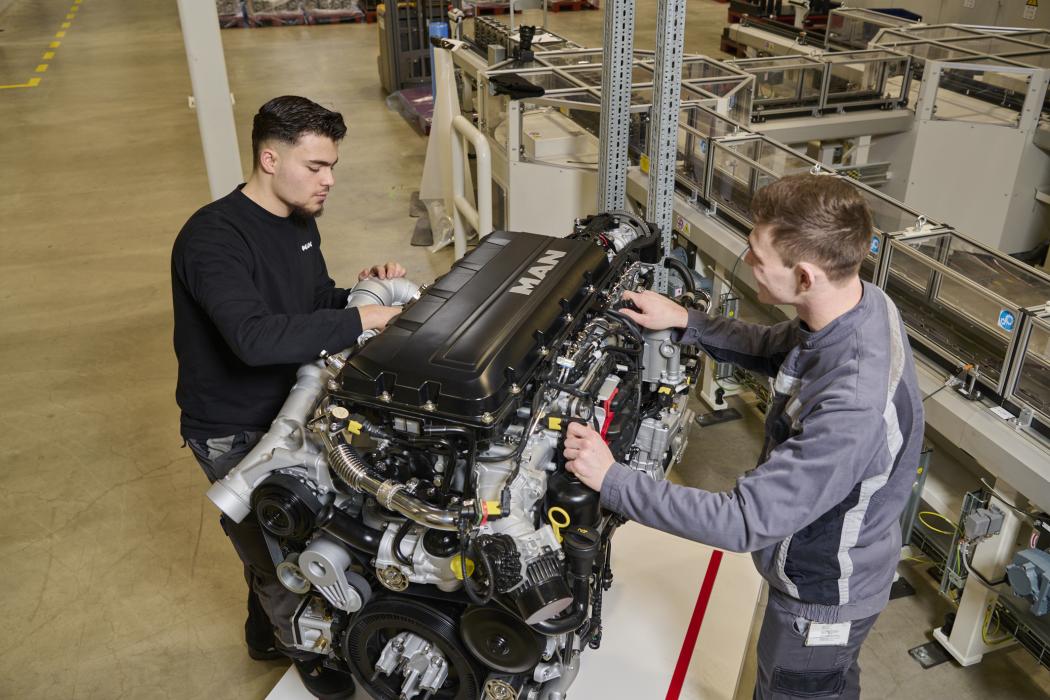
The D30 is set to replace the proven D26 "bread and butter" engine in the coming years. In the TGX semi-trailer trucks, the new engine is already the standard, and the chassis will gradually follow.
Where does the D30 actually come from? While the D26 was still a traditional MAN development, the D30 is a product of the Traton group under the VW umbrella, alongside its sister company Scania. Scania released a technically similar engine under the moniker "Super" a few years ago. However, it is still legitimate to describe the D30 as a MAN product because it is assembled at MAN's engine plant in Nuremberg.
In his webinar, Harald Wieching also explains why the D30 has to replace the
proven D26: The stricter emission regulations expected with Euro VII could only be met by the D30: increased compression (23:1 compared to 21:1 in the D26) boosts the efficiency of the 12.8-liter six-cylinder engine to 50 percent thermal efficiency. Reduced internal friction and demand-controlled auxiliary units also play a role.
However, the D30 also burns significantly hotter, which results in an increase in nitrogen oxides. MAN addresses this conflict with a double SCR injection. The AdBlue consumption only slightly increases as a result, from just under 8% of diesel consumption to 10.1% in the D30. Overall, the D30 shows a four percent reduction in consumption or CO2 emissions.
Wieching states that the new D30 reaching its maximum torque significantly earlier
must inevitably lead to an adapted drivetrain. For MAN, this is not a problem, as they can fall back on the 14-speed Tipmatic. This automated transmission, also fundamentally developed by Scania, is always used as an overdrive version. In this, the highest gear (12) is long geared (0.78), and the direct drive gear is the eleventh. One reaches 14 gears by counting the two lowest gears as 13 and 14.
This opens up completely new possibilities for always driving the engine within its optimal consumption range. If high load is required, the engine electronics favor the eleventh, direct gear. This gear is the most economical under high load due to the least gear meshing. Under partial load or in thrust,
one benefits more from a long geared gear because it builds up less drag torque in thrust. Thus, the MAN with the D30 always shifts to the most efficient gear when under load. The overdrive practically simulates a very long axle, which is advantageous for free rolling and low load, for example, on level ground.
In terms of engine braking performance, the D30 represents progress as well. Its cylinder head, controlled by two overhead camshafts, allows for the implementation of a valve lever engine brake. This provides considerable engine braking power, making it possible to forgo an additional retarder in many moderate topography applications. rod
All past sessions are available for viewing as a video stream, after registration, on conference-days.de.